[2019 CVPR] Adaptive Transfer Network for Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification
Table of content (full-version) [paper]
Summary
- Unsupervised reid 논문
- Domain gap을 줄이기 위해서 여러개의 본질적인 factor로 구분한 첫 논문
- Source와 target의 domain gap을 줄이기 위한 전략으로 divide and conquer 방식 제안
- Factor-wise sub-transfers: 특정 factor(illumination, resolution, camera-view)에 집중하여 style을 변형
- Adaptive ensemble method: 여러개의 factor-wise transfer에 가중치를 부여하며 융합
Architecture
- Problem formulation
- Source: pairwise label 있음, 이를 target처럼 변경한 다음 supervised 방식으로 학습
- Target: pairwise label 없음, 영상 스타일을 제공
- Objective: 소스 영상을 타켓처럼 변형한 다음, Jensen-Shannon divergence를 통해 데이터 분포를 유사하게 만든다.
[전체 아키텍처]
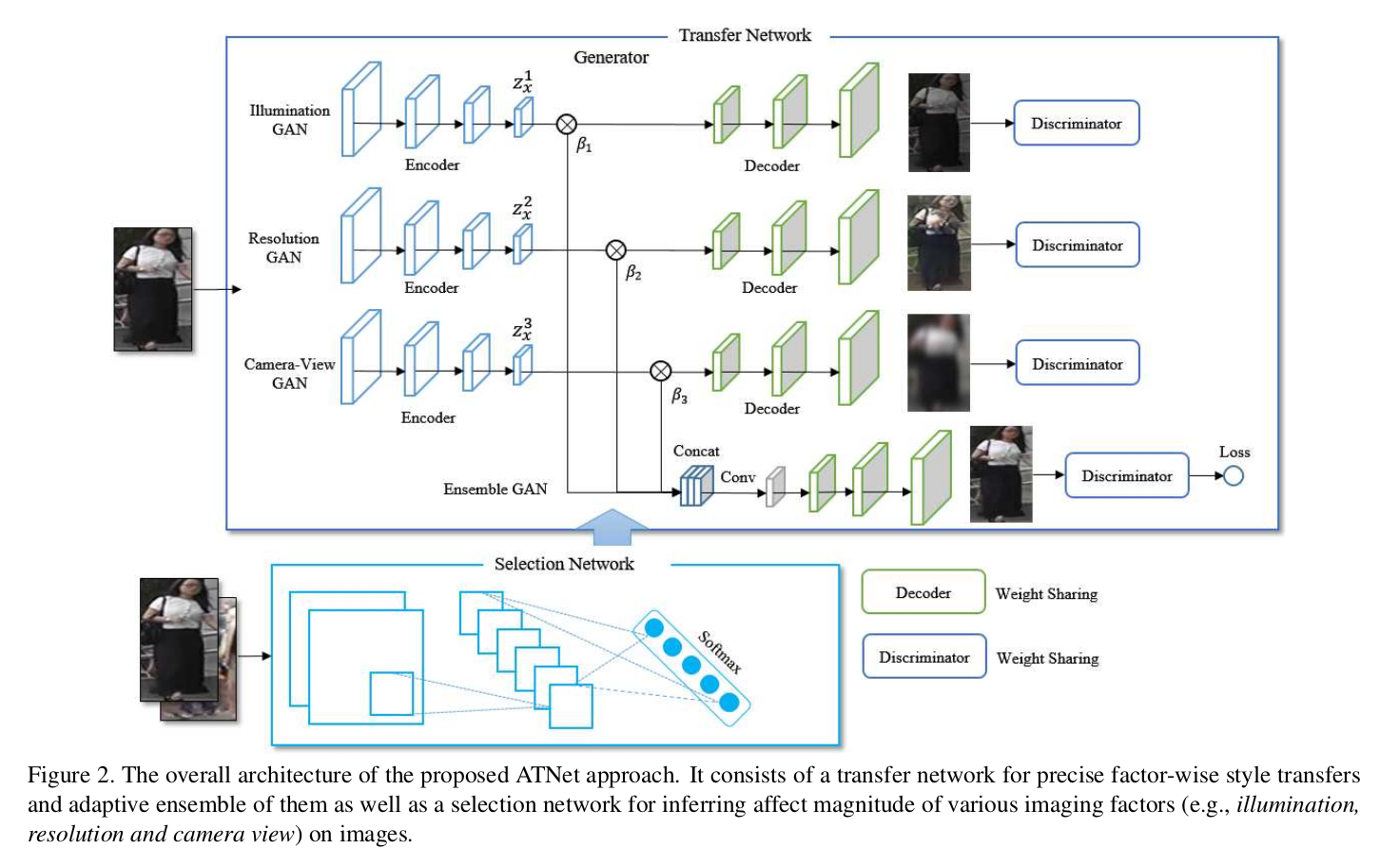
- 전체 아키텍처
- 세 개의 모듈로 구성 (factorGAN 3개, ensemble GAN, selection network)
- Transfer network (factorGAN, ensemble GAN)
- 공통구조
- CycleGAN (2개의 generator-generator pairs) 기반이지만 (adversarial loss, cycle-consistent loss, identity mapping loss)를 사용하지는 않음
- 실제로 [2]와 비슷
- Loss:
- Adv: 변환된 source 데이터 분포를 target 데이터 분포에 매칭
- Cyc: 원본 샘플이 두 번의 cycle 변환 이후에도 복원되도록
- Ide: 원본과 변환된 샘플 사이의 color consistency
- FactorGAN
- 가공된 Source data를 이용하여 아래의 모듈들이 각각의 목표를 갖도록 미리 학습
- 이후에 source-target 쌍으로 Pretrained factorGAN 모듈들을 추가 학습
- 가공 방법: Illumination (random gamma correation) / Resolution (downsample) / Camera-view (2 images from different camera in S)
- Illumination GAN: 기본 loss + illumination constraint (using illumination insensitive feature) [3]
- Resolution GAN: 기본 loss + resolution constraint (using resolution-insensitive feature) [4]
- Camera-view GAN: 기본 loss만 이용
- 각각 변환된 영상에 discriminator를 달아서 real/fake 판단
- Ensemble GAN
- Factor GAN 의 latent vector 들과 selection network에서 추출된 가중치 이용하여 concatenate
- z를 3개 concat했으므로 다시 1by1 convolution를 이용하여 dimension을 낮춘 후 decoder를 통해 최종 영상 복원
- 변환된 영상에 discriminator를 이용하여 real/fake 판단
- Jensen-Shannon divergence를 이용하여 factorGAN에 의해서 추출된 latent vector 쌍(총 3개, 경우의 수 3C2) 사이의 데이터 분포 맞춤
- 최종 loss는 기본 loss + JS loss
- 모듈구조
- Decoder: 9개의 residual block, 4개의 conv layer [5]
- Discriminator: 70 70 PatchGANs [6]
- Detailes can be found in [7]
- Decoder, discriminator는 웨이트 공유, encoder만 다른 웨이트
- 공통구조
- Selection network
- FactorGAN 사이의 가중치 계산하는 네트워크
- Training
- 입력(학습): 한 쌍의 source + target 영상
- 구조: 4개의 convolution + 1개의 FC (6-dim) 2개의 softmax
- 출력: 두 쌍의 이미지에 대한 3+3개의 가중치
- loss: S-T 영상 pair가 입력되면 transfer network로부터 계산된 가중치를 ground truth로 간주하고 이 정보와 MSE를 사용
- Feature learning
- 위의 네트워크에 의해서 target-like source 영상들이 생성
- 이를 통해 supervised 방식과 같이 학습
- ResNet50(2048-dim), GoogleNet(4096-dim) 이용
Experimental results
- Ablation studies
- FactorGAN을 하나씩 빼 보았을 때, illumination GAN을 뺀 것이 가장 성능이 낮았다.
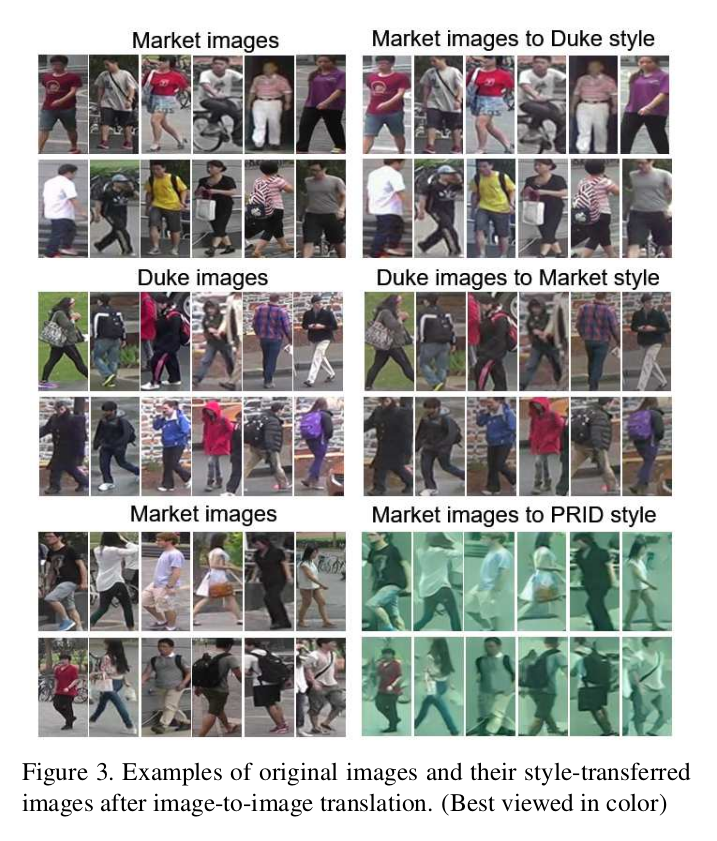
- 영상 변환 예시
[영상 변환 결과 예시]

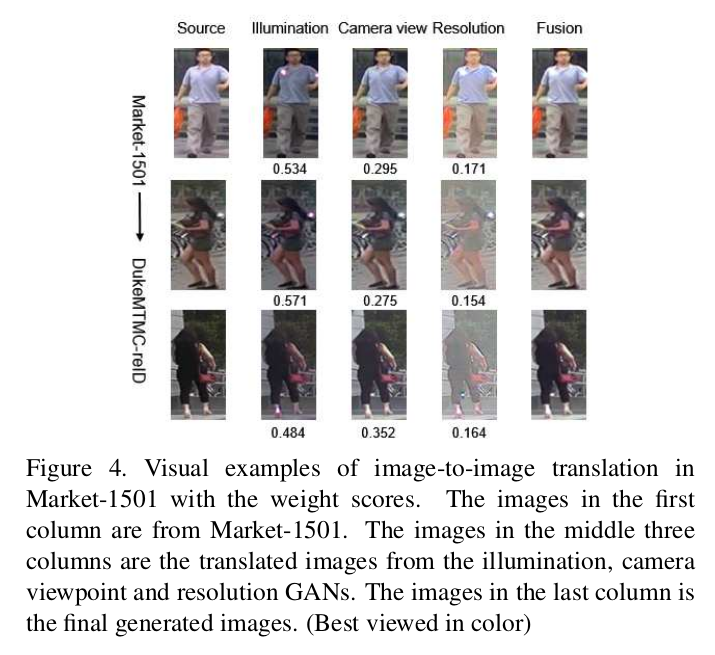
- 영상 융합 예시
[영상 융합 결과 예시]

Comments
- 영상 융합 결과 예시 영상을 볼 때, 각 factorGAN 사진을 보면 illumination만 바뀐 것 같은데..
References
[1] Liu, Jiawei, et al. “Adaptive Transfer Network for Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification.” Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019.
[2] Taigman, Yaniv, Adam Polyak, and Lior Wolf. “Unsupervised cross-domain image generation.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.02200 (2016).
[3] Zhang, Taiping, et al. “Face recognition under varying illumination using gradientfaces.” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 18.11 (2009): 2599-2606.
[4] Ledig, Christian, et al. “Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network.” Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2017.
[5] He, Kaiming, et al. “Deep residual learning for image recognition.” Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016.
[6] Isola, Phillip, et al. “Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks.” Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2017.
[7] Zhu, Jun-Yan, et al. “Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks.” Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2017.