[2019 CVPR] Unsupervised Person Image Generation with Semantic Parsing Transformation
Table of content (full-version) [paper] [github]
Summary
- Unsupervised (unpaired) + end-to-end pose-guided person image generation (challenging due to non-rigid deformation)
- 기존의 rock-hard direct mapping 방법을 두개의 가능한 서브 task로 분할
- Semantic generative network: non-regid deformation learning을 간단화하기 위해서 target pose에 따라서 semantic parsing map을 변환
- Appearance generative network: 변환된 semantic parsing map에 semantic-aware texture를 합성 (semantic-aware style loss 이용)
- 기타 방법들: semantic parsing을 위한 pseudo labeling 방법, 학습에 사용되는 cycle consistency, end-to-end manner
Motivation
- 기존의 방법들
- Paired supervision을 많이 사용 data 부족 문제로 unpaired 방법 발전 (그러나 성능은 아직)
- Disentanglement 방식도 제안 non-rigid human body deformation and clothing shape를 무시하면 좋은 성능 못냄
- 완전한 unsupervised 방식(unpaired)의 어려움
- 인간의 몸은 non-rigid deformation이므로 공간적으로 정렬되지 않은 몸을 변환하는 것은 현재의 conv기반 네트워크에서 어렵다
- 다른 포즈를 생성하는 동안 옷의 특성을 보존하기 어렵다
- pair 영상을 활용하지 못하므로 효율적인 학습 목적을 달성하기 힘들다
- 이를 해결하기 위해 비교적 쉬운 사람 영상과 semantic parsing 사이의 관계를 이용한다.
Architecture
[Notation]
| Symbol | Mean |
|---|---|
| source image | |
| predicted source image by mapped-back (cycle consistency) | |
| predicted target image | |
| source pose (2D pose by OpenPose[2] 18-dimension heat map) | |
| target pose (pseudo pose by affine transformation) | |
| source pose mask (same definition in [3]) to help generate continuous semantic maps | |
| target pose mask (pseudo mask) | |
| source semantic map (Human parser[4]: 10 labels, ) | |
| target semantic map (pseudo ground truth) | |
| predicted source semantic map by mapped-back (cycle consistency) | |
| predicted target semantic map | |
| semantic generator | |
| semantic map encoder | |
| pose encoder | |
| semantic map generator | |
| semantic map discriminator | |
| appearance generator | |
| appearance encoder | |
| semantic map encoder | |
| appearance generator | |
| appearance discriminator | |
| face discriminator |
Overall framework
- Unsupervised 방식 ({, } 를 이용하지 않음)
- 기본적으로 보유한 것: {}
- Additional 추정한 것: {, , }
- Pseudo labeling한 것: {, , }
- 찾아야 하는 것: {, }, {, } for cycle consistency
- 순방향:
- 역방향:
[전체 프레임워크]
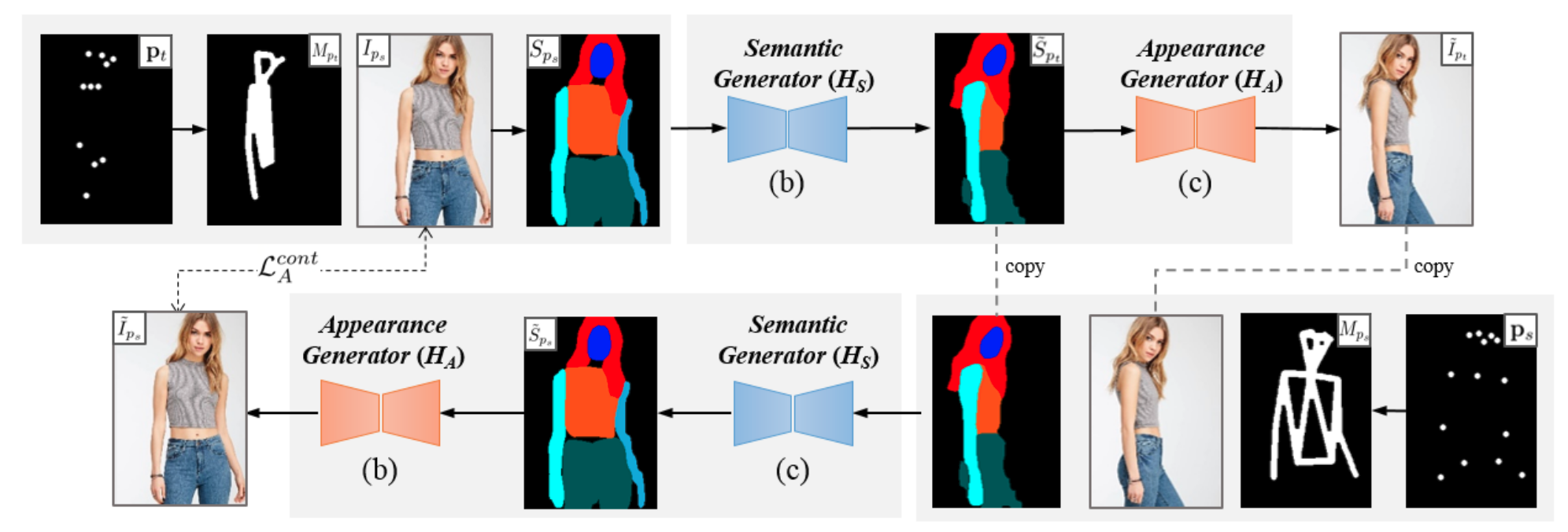
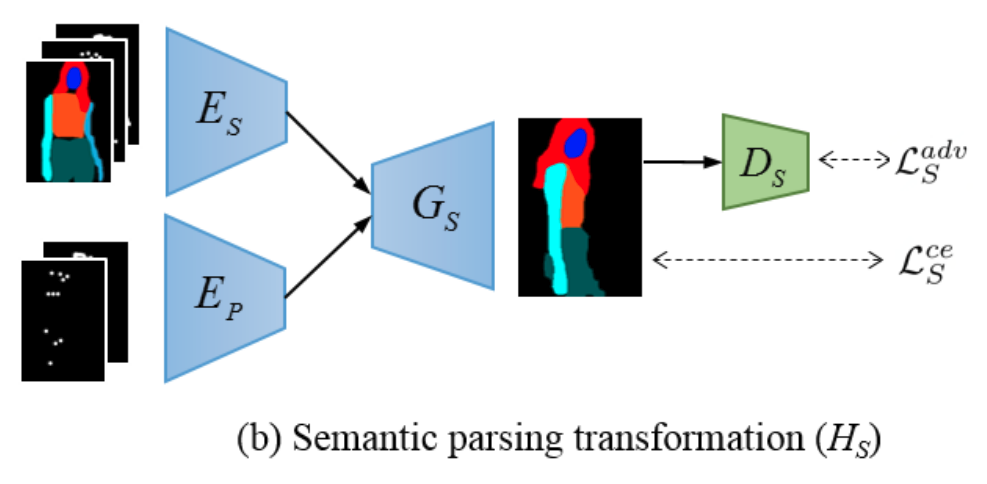
Semantic parsing transformation
$$\tilde{S}_{P_t} = G_S (E_S (S_{P_s}, P_s, M_{P_s}), E_P (P_t, M_{P_t}))$$
- Semantic map을 출력하기 위해서 Generator 뒤에 각 픽셀마다 softmax activation function을 적용
- 이 따로 없기에 학습에 용이하도록 pseudo labeling 적용 ()
- 에는 옷 정보가 없으므로 를 기반으로 를 생성한다.
- [5] 에서 사용한 것처럼 10개의 rigid body subparts를 나누어 binary mask를 형성한다.
- 이 binary mask와 affine transformation을 이용하여 새로운 포즈 새로운 semantic mask를 형성한다. (이때 너부 포즈가 비슷하면 배제)
$$S_{P^*_t} = \arg\min_{S_p} \sum^{10}_{j=1} \left \| B^j_p \bigotimes S_p - f_j (B^j_{P_s} \bigotimes S_{P_s}) \right \|^2_2$$
[Semantic generative network]
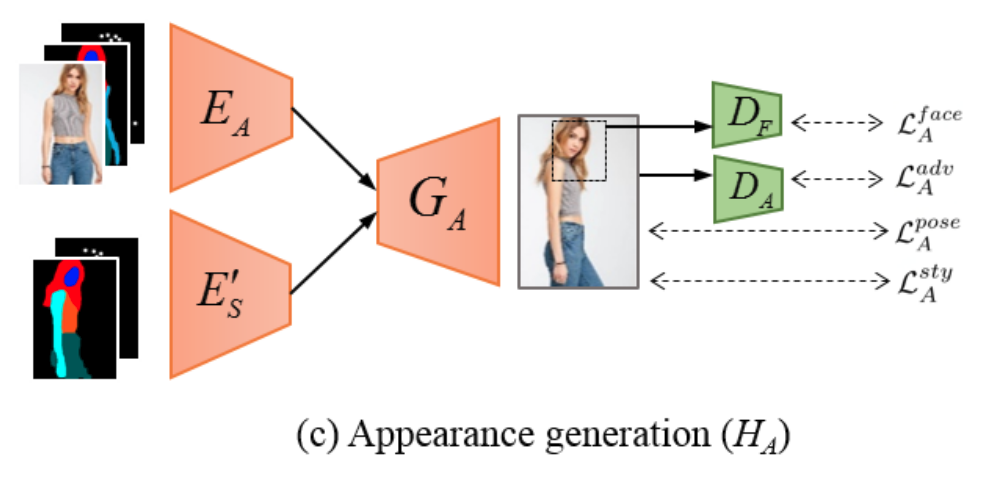
Appearance generation
$$\tilde{I}_{P_t} = G_A (E_A (I_{P_s}, P_s, S_{P_s}), E'_S (P_t, \tilde{S}_{P_t}))$$
- [5] 를 사용하여 affine transformation을 통해 pseudo labeling을 하는 부분과 softmax를 사용하는 부분 빼고는 동일한 구조이다.
- Ground truth가 없기 때문에 cycle consistency를 이용한다.
[Appearance generative network]
Loss function
- Adversarial loss:
- Semantic generative network
- Cross entrophy loss
$$L^{ce}_S = - \left \| S_{P^*_t} \bigotimes \log(\tilde{S}_{P^*_t}) \bigotimes (1+M_{P^*_t}) \right \|_1$$
- Pseudo label에 의해서 paired data 생성 </p>
- 사용:
- 가 잘 추정되도록 pixel-level accuracy 측정
- Adversarial loss
$$L^{adv}_S = L^{adv} (G_S \circ (E_S, E_P), D_S, S_{P^*_t}, \tilde{S}_{P^*_t})$$
- 사용: , generator, discriminator
- 가 생성된 semantic map이 실제인지 아닌지 구분
- Cross entrophy loss
- Appearance generative network
- Adversarial loss
$$L^{adv}_A = L^{adv} (G_A \circ (E_A, E'_S), D_A, I_{P_s}, \tilde{I}_{P_s}) + L^{adv} (G_A \circ (E_A, E'_S), D_A, I_{P_s}, \tilde{I}_{P_t})$$
- 사용: , generator, discriminator
- 가 생성된 영상이 실제인지 아닌지 구분 (Source image와 생성된 target image 사이) 그리고 (source image와 생성된 source image사이)
- Pose loss
$$L^{pose}_A = \left \| \mathcal{P}(\tilde{I}_{P_s}) - P_s \right \|^2_2 + \left \| \mathcal{P}(\tilde{I}_{P_t}) - P_t \right \|^2_2 $$
- 사용: , pose detector ,
- [6]에서처럼 생성된 영상들 , 에 pose detector에 통과한 결과가 와 비슷한지 확인
- Content loss
$$L^{cont}_A = \left \| \Lambda(I_{P_s}) - \Lambda(\tilde{I}_{P_s}) \right \|^2_2$$
- 사용: , VGG feature map
- Source image의 cycle consistency를 보증하기 위해 ImageNet에서 학습한 VGG16 모델의 conv2_1 layer를 통해 복원된 영상과의 텍스처 사이를 확인
- Sytle loss
$$L^{sty}_A = L^{sty}(I_{P_s}, \tilde{I}_{P_t}, S_{P_s}, \tilde{S}_{P_t}) + L^{sty}(\tilde{I}_{P_s}, \tilde{I}_{P_t}, \tilde{S}_{P_s}, \tilde{S}_{P_t})$$
$$L^{sty}(I_1, I_2, S_1, S_2) = \sum^L_{l=1} \left \| \mathcal{G}(\Lambda(I_1) \bigotimes \Psi_l (S_1) ) - \mathcal{G}(\Lambda(I_s) \bigotimes \Psi_l (S_s)) \right \|^2_2$$
- 사용: , , gram matrix , down-sampling
- (Source image와 생성된 target image 사이) 그리고 (생성된 source image와 생성된 target image 사이) 에서 스타일이 유지되는지 보증하기 위해서 semantic-aware style loss 제안 gram matrix를 이용
- [6]은 pose joint의 텍스처가 유지되도록 patch-sytle loss를 제안하였으나 joint주변 텍스쳐는 자세에 따라서 변한다는 것과 main 몸통 부분의 텍스처는 무시된다는 문제점을 갖음
- Face loss
$$L^{face}_A = L^{adv} (G_A \circ (E_A, E'_S), D_F, \mathcal{F}(I_{P_s}), \mathcal{F}(\tilde{I}_{P_s})) + L^{adv} (G_A \circ (E_A, E'_S), D_F, \mathcal{F}(I_{P_s}), \mathcal{F}(\tilde{I}_{P_t}))$$
- 사용: , , face extraction
- 가 생성된 semantic map이 실제인지 아닌지 구분
- (Source image와 생성된 target image 사이) 그리고 (source image와 생성된 source image 사이)에서 얼굴 특징이 비슷한지 확인
- Market-1501에서는 해상도가 낮아 적용하지 않음
- Adversarial loss
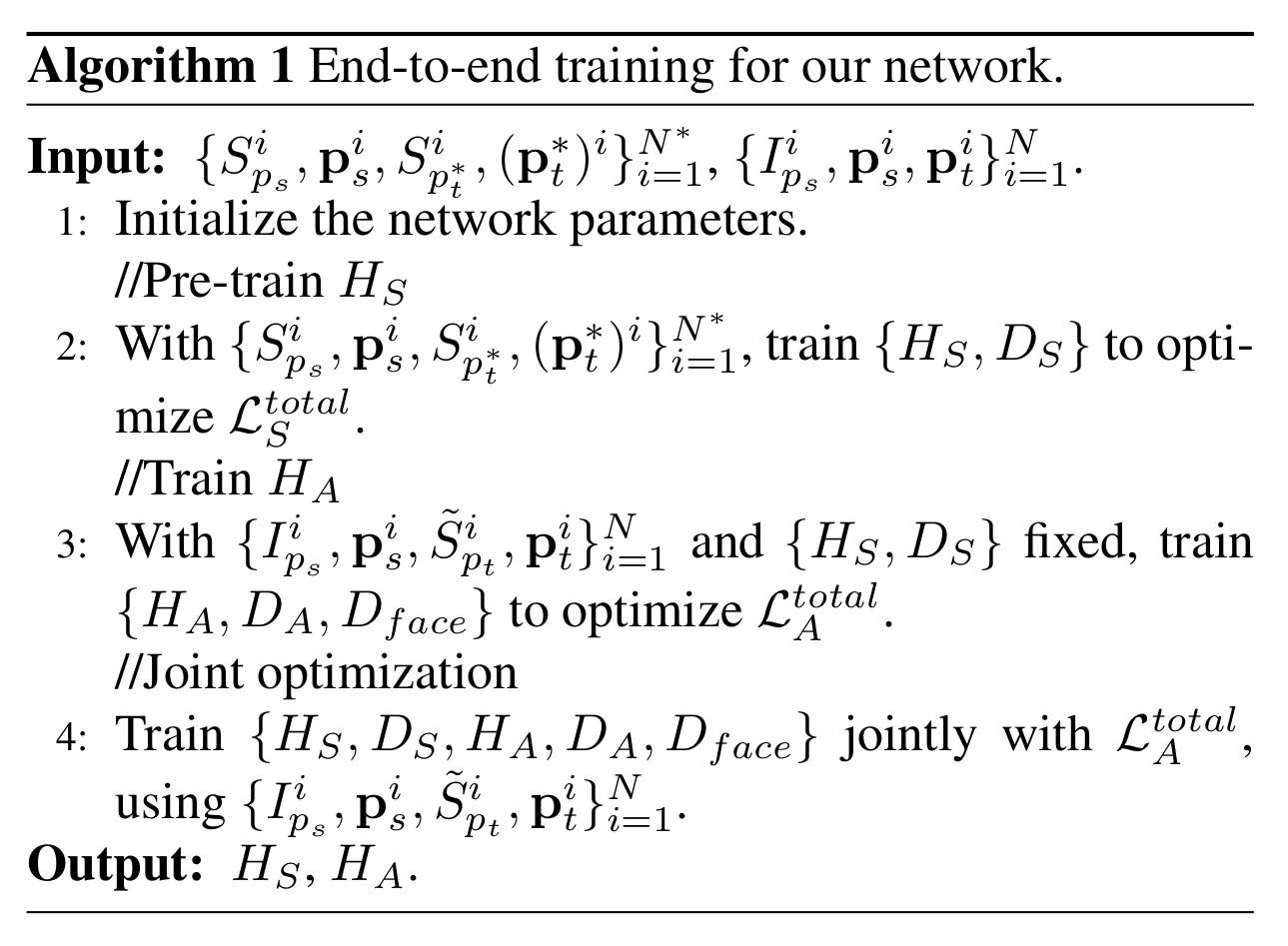
End-to-end training
- 만약 독립적으로 학습을 한 다음에 합치면 아래와 같은 문제들이 발생
- Searching error: pseudo label 이 정확하지 않는 문제
- Parsing error: human parser 가 정확하지 않는 문제
- 따라서 따로 학습한 뒤에 joint optimization을 통해 두 task를 융합시켜 end-to-end로 학습
[End-to-end training algorithm]
Implementation details
- Batch size: Deep fashion (4) Market-1501 (16)
- Semantic map prediction: Deep fashion (128 128에서 수행한 뒤 upsample), Market-1501 (128 64에서 그대로 수행)
Experimental results
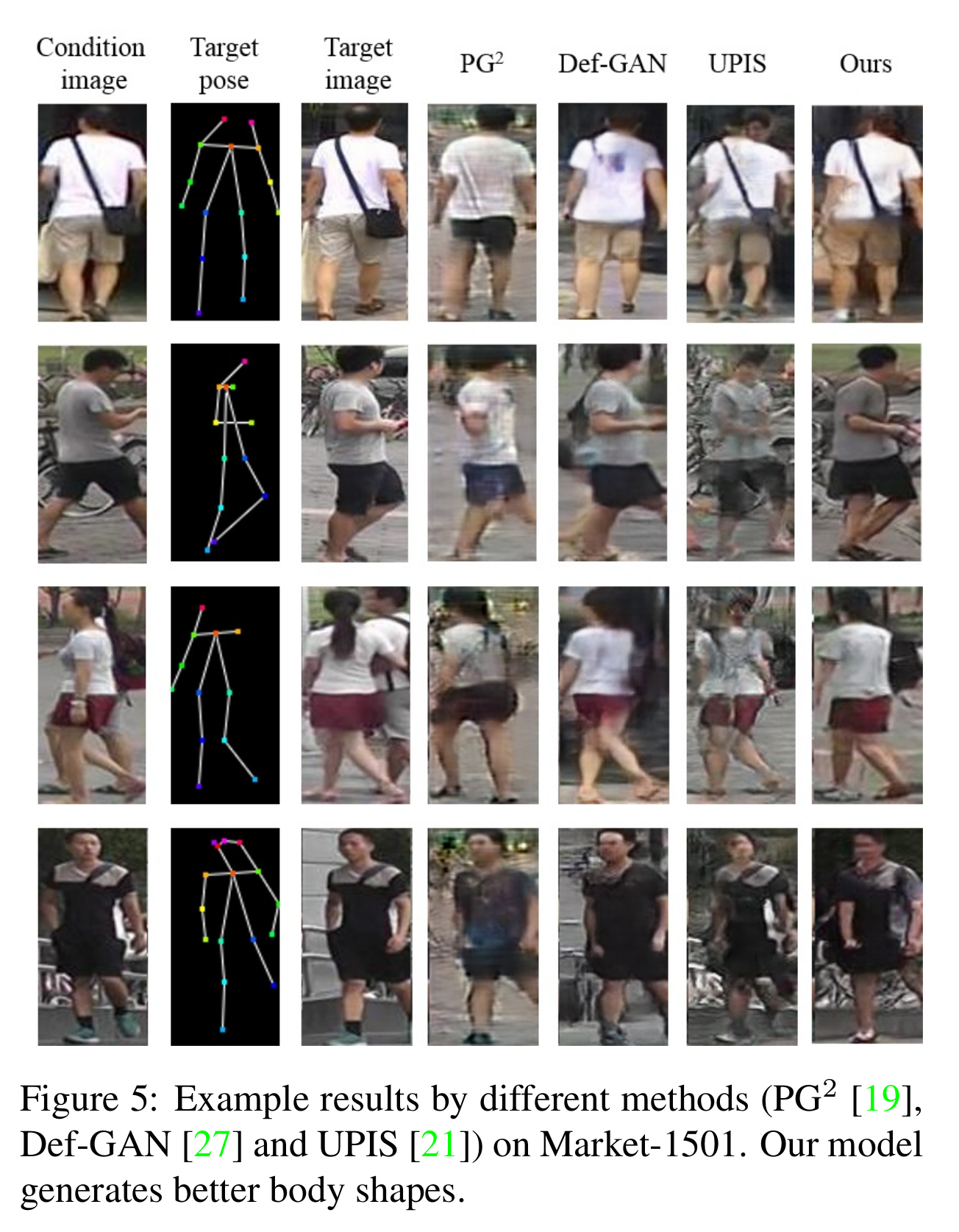
- 사람 생성 모델 성능 비교
[사람 생성 모델관련 여러가지 방법들과의 성능비교 (Deep fashion)]
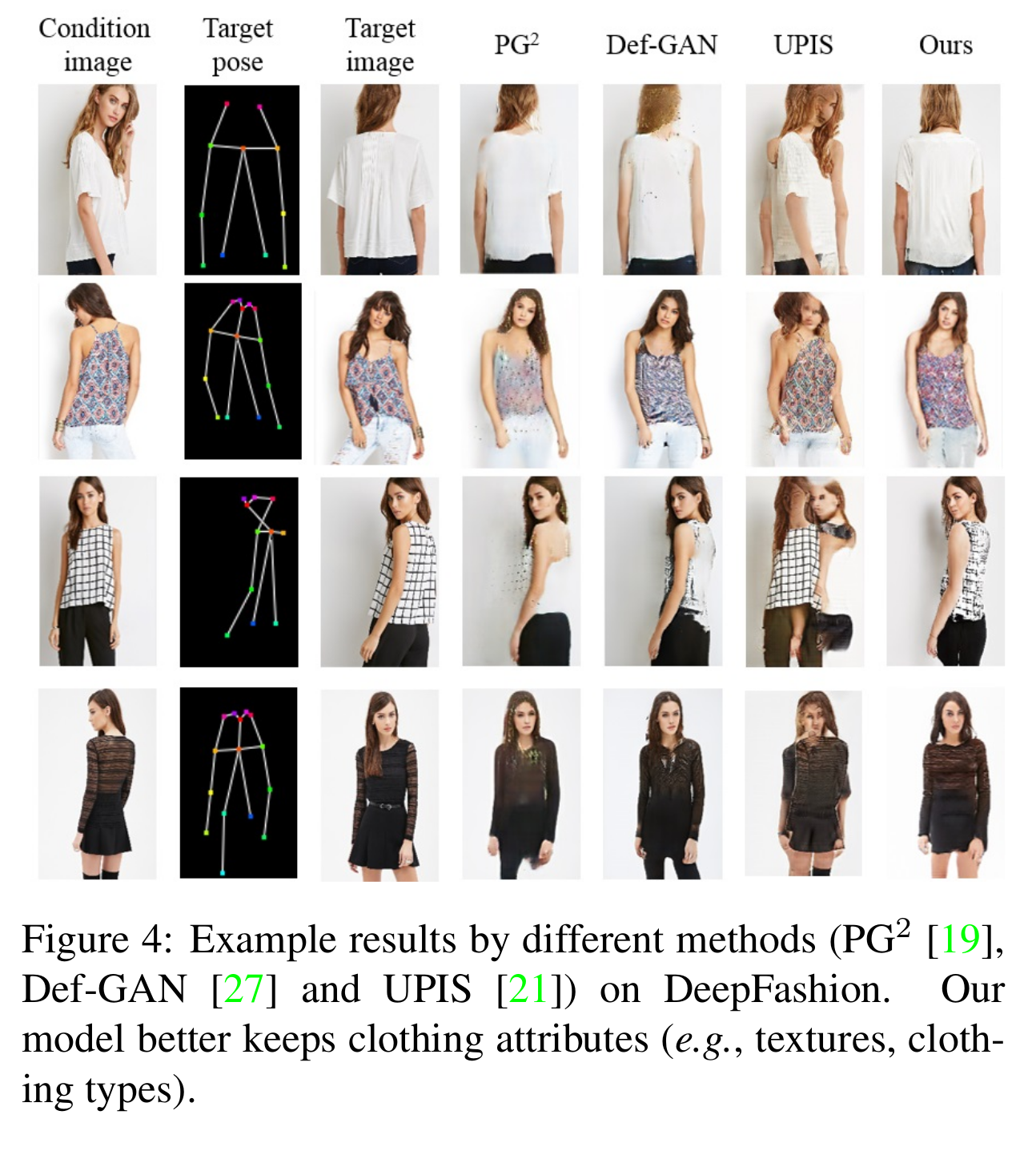
[사람 생성 모델관련 여러가지 방법들과의 성능비교 (Market-1501)]

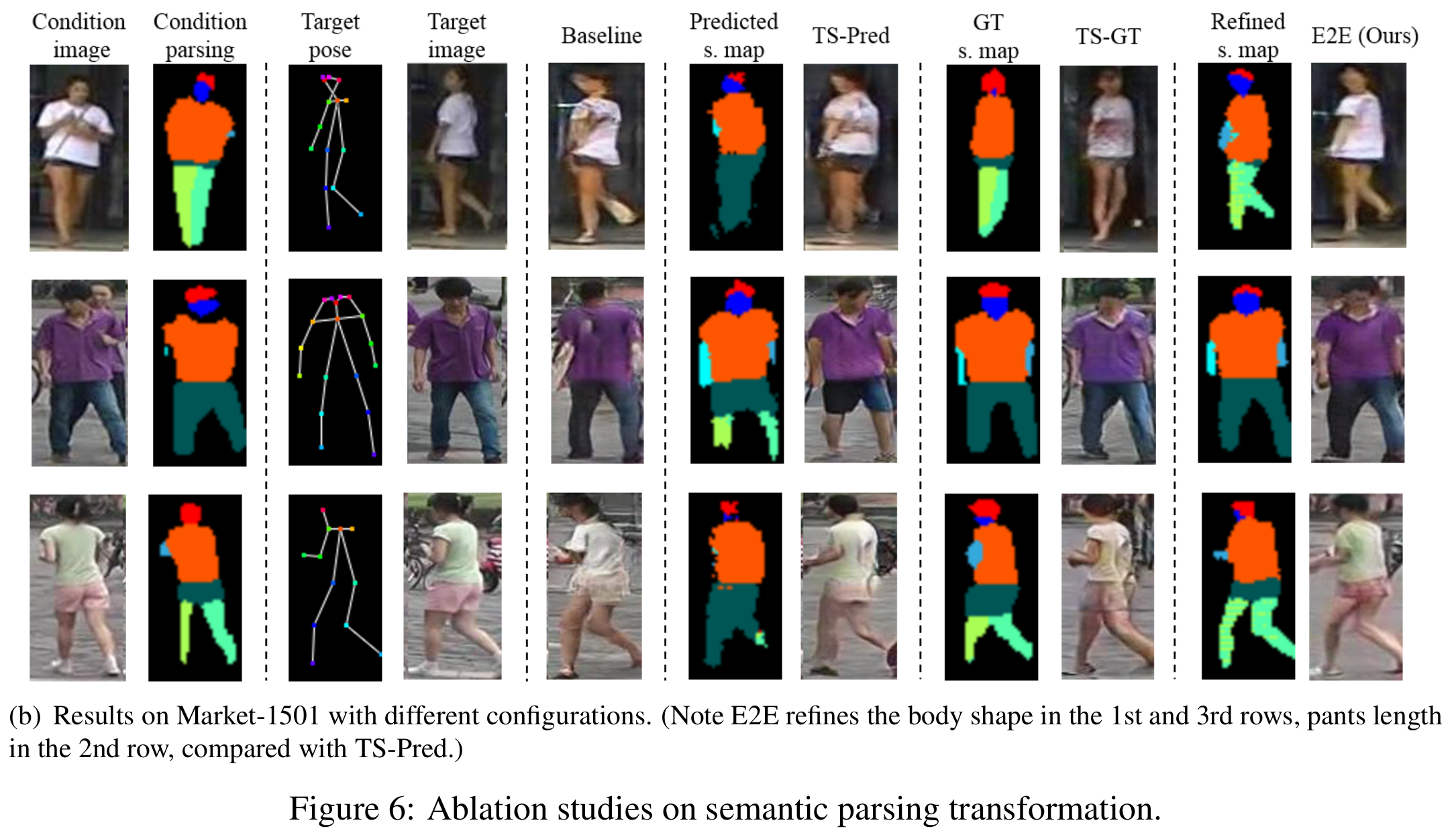
- Ablation study
- Network training (market-1501에서는 GT보다 E2E가 좋았는데 그 이유는 해상도 때문)
- Baseline: semantic parsing 없이 appearance generative network만 사용. mask-style loss 사용(semantic-aware style loss에서 semantic map대신에 body part mask를 사용)
- TS-pred: 두 generative network를 독립적으로 학습 (two-stage)
- TS-GT: 마찬가지로 two-stage로 접근하며, pseudo label 대신에 human parser에 의한
- E2E: 제안하는 방법
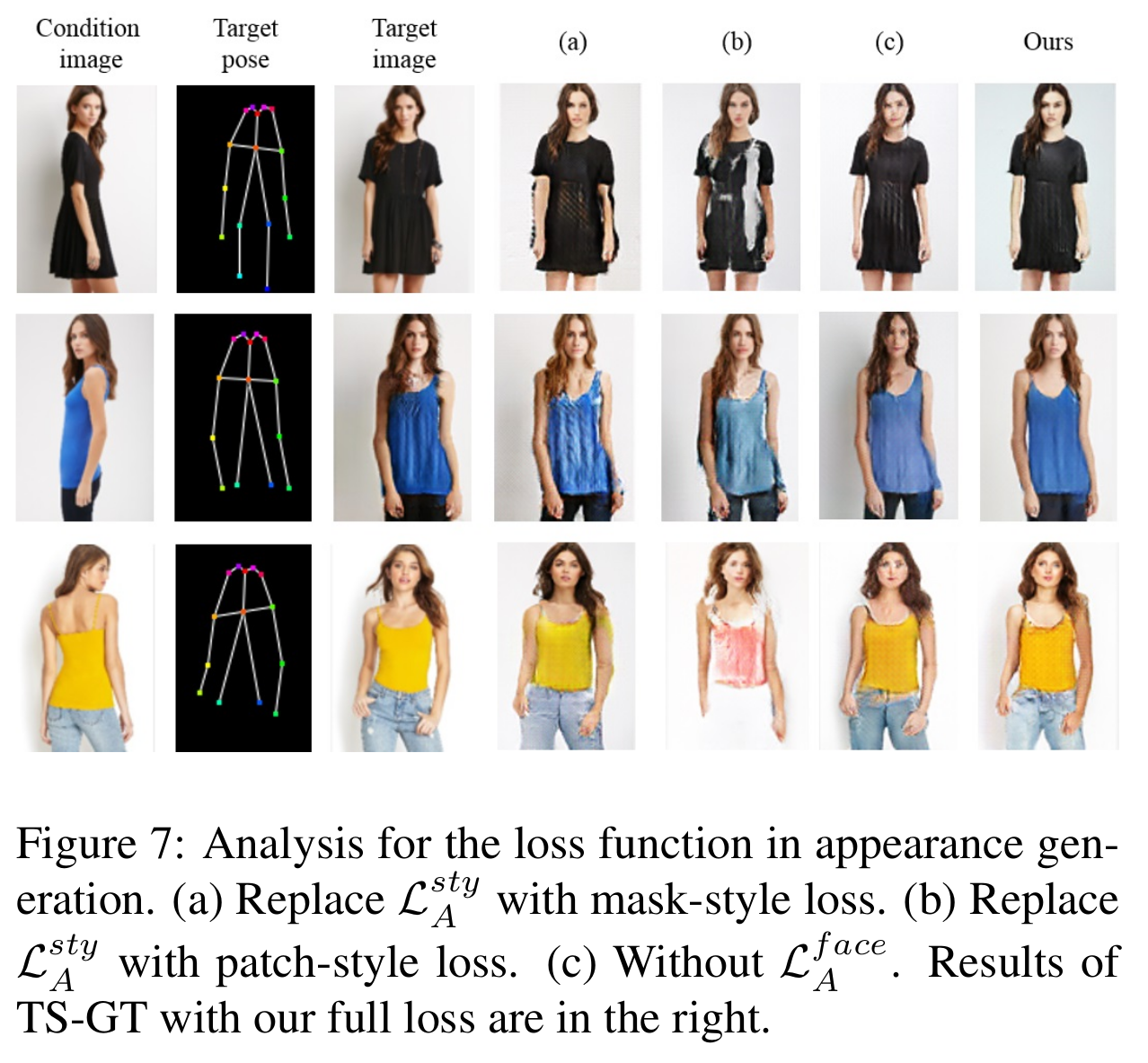
- Loss function (semantic map에 영향을 받지 않기 위해 TS-GT에서 시작)
- (a) Semantic-aware style loss 대신에 mask-style loss
- (b) Semantic-aware style loss 대신에 patch-style loss
- (c) Semantic-aware style loss는 있지만 Face adversarial loss 부재
- Network training (market-1501에서는 GT보다 E2E가 좋았는데 그 이유는 해상도 때문)
[Ablation study (network training)]
[Ablation study (loss function)]
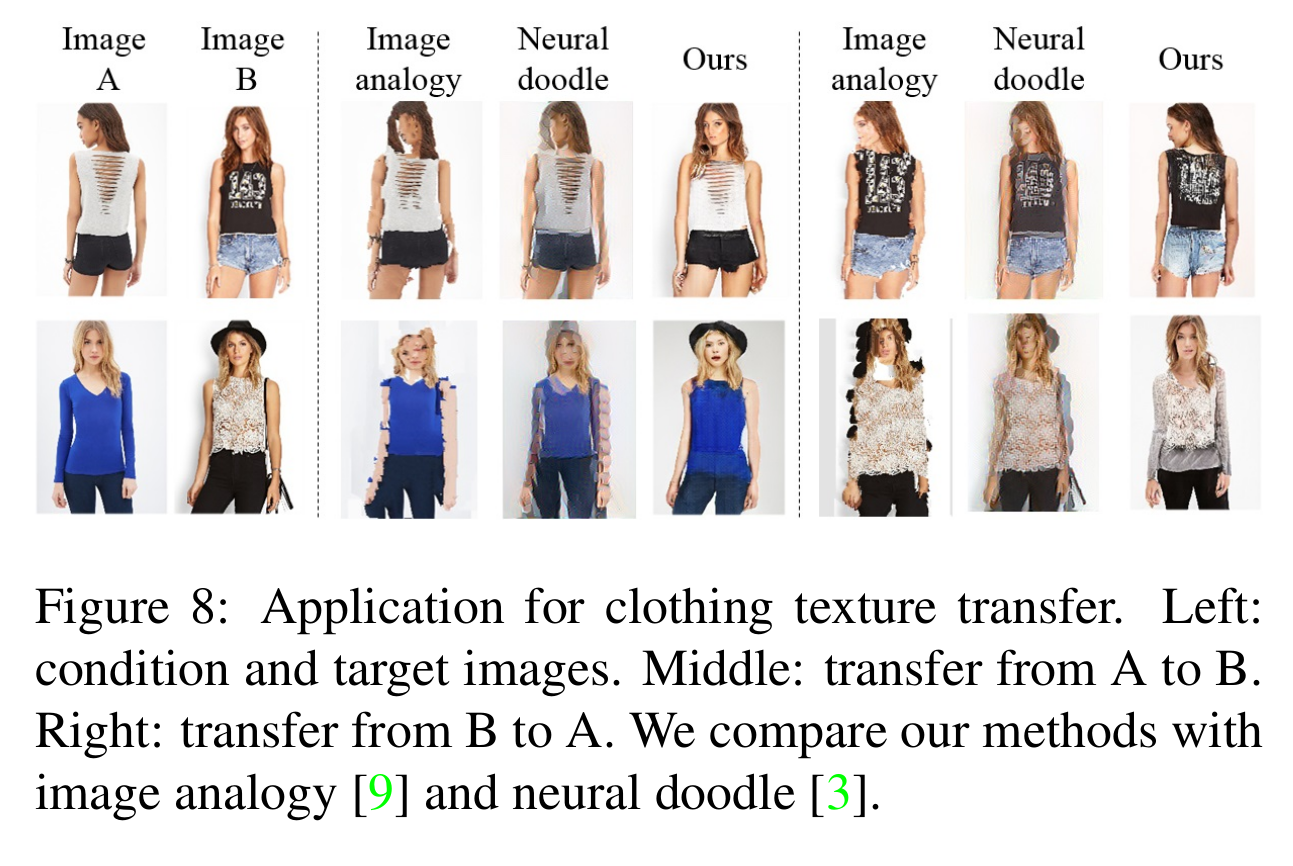
- Application
- Clothing texture transfer: 영상 2개에 대해서 semantic parsing 결과가 주어졌을 때, A의 옷 형태를 B의 semantic map에 입히는 응용
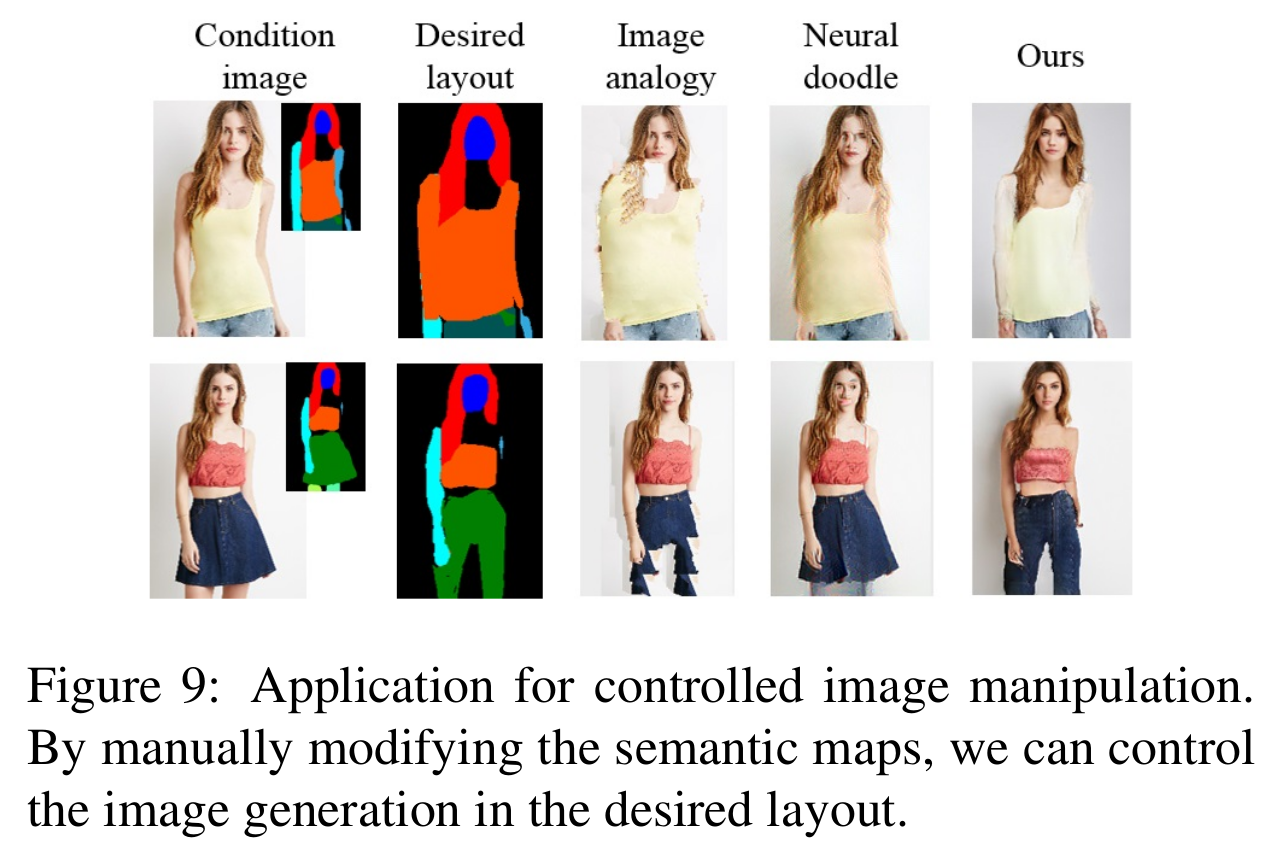
- Controlled image manipulation: semantic map을 수정하여 원하는 layout을 얻는 응용
[Texture transfer 응용]
[Controlled image manipulation 응용]
- Failure case
- 첫번째 줄은 parsing error
- 두번째 줄은 searching error (희귀한 포즈로 인해)
[Failure case]

Comments
- Future work으로는 human parser까지 같이 학습시키는 방향으로 (왜냐하면 parsing error)
References
[1] Song, Sijie, et al. “Unsupervised Person Image Generation with Semantic Parsing Transformation.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.03379 (2019).
[2] Zhe Cao, Tomas Simon, Shih-En Wei, and Yaser Sheikh. Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017.
[3] Liqian Ma, Xu Jia, Qianru Sun, Bernt Schiele, Tinne Tuytelaars, and Luc Van Gool. Pose guided person image generation. In Proc. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017
[4] Ke Gong, Xiaodan Liang, Dongyu Zhang, Xiaohui Shen, and Liang Lin. Look into person: Self-supervised structure sensitive learning and a new benchmark for human parsing. In Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017.
[5] Aliaksandr Siarohin, Enver Sangineto, St´ephane Lathuili`ere, and Nicu Sebe. Deformable gans for pose-based human image generation. In Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018.
[6] Albert Pumarola, Antonio Agudo, Alberto Sanfeliu, and Francesc Moreno-Noguer. Unsupervised person image synthesis in arbitrary poses. In Proc. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018.