[2017 CVPR] Disentangled representation learning gan for pose-invariant face recognition
Table of content (full-version) [paper] [github]
Summary
- Pose-invariant identity representation을 학습함과 동시에 임의의 pose에 대한 얼굴을 생성하는 기술
- Face recognition 분야에서 두 영상 사이의 pose discrepancy는 인식의 어려움을 준다.
- DR-GAN은 입력 영상에 대한 pose정보를 가진채 합성하고자 하는 얼굴의 pose 정보를 직접 부여함으로써 pose에 대한 disentanglement를 수행한다.
- 입력으로 한 장이 아닌 여러장의 영상을 넣을 수 있다. (single image DR-GAN, multi image DR-GAN)
Architecture
- 기존 GAN과 유사하지만 다른점
- Generative representation: (동일사람 여러 얼굴 생성) 얼굴 영상을 위한 identity 표현을 학습하고 이는 여러 변수들(z, pose)과 합쳐져서 decoder에서 동일 사람에 대해서 여러가지 얼굴 영상을 생성한다.
- Disciminative representation: (여러 변수에 무관한 특징 학습) 인코더가 동일 사람에 대해서 여러 변수가 있더라도 특징적인 표현을 잘 학습하기 위해서 pose나 illumination과 같은 사이드 정보를 이용함으로써 변수에 대한 명확한 disentanglement를 수행한다.
- 다른 GAN과의 차이점
- Conditional GAN [2,3]: CGAN에서는 D가 실제 이미지 + mis-matched condition이 fake class로 분류되게 학습되는 반면, DRGAN에서의 D는 실제 이미지 + 해당 클래스가 해당 클래스로 분류되게 학습한다.
- Semi-supervised GAN [4]: 개의 클래스를 분류한다는 점에서 D loss가 비슷하지만, DR-GAN은 G를 encoder-decoder구조로 연장했고 D에서는 additional side 정보(pose)를 추가하였다.
- Adversarial autoencoder [5]: AAE는 부여된 prior 분포와 비슷하게 latent representation을 학습하지만, DR-GAN의 encoder-decoder구조는 분별적인 identity를 학습한다. 또한 AAE에서의 D는 real/fake 분포만 판단하지만, DR-GAN에서의 D는 real/fake 뿐만 아니라 identity와 pose도 분류한다.
[전체 프레임워크]
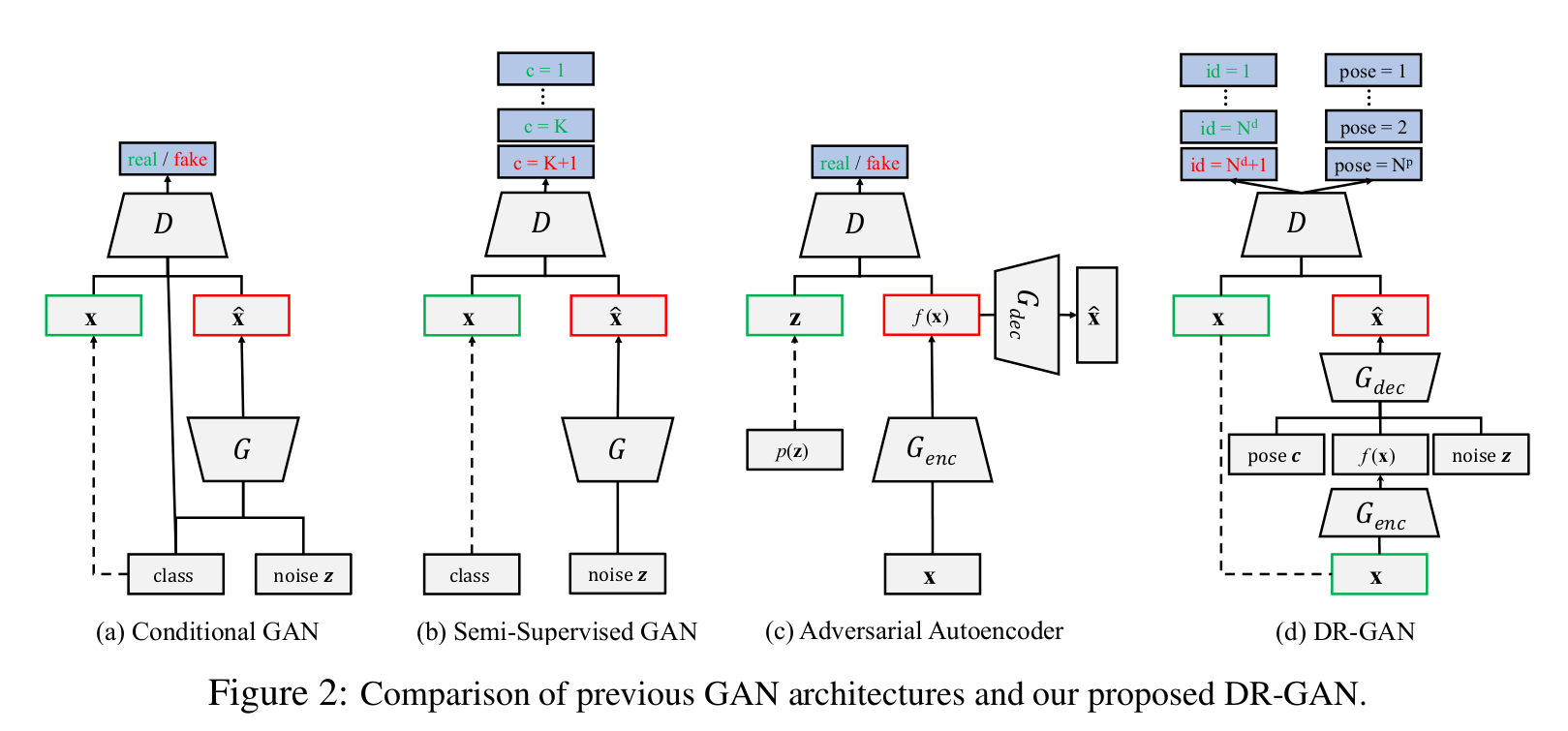
Discriminator
$$D = [D^d, D^p] \in \mathbb{R}^{N^d+N^p+1}$$
- 와 동일한 구조에 추가로 -dim fc-layer 적용하여 사용
- Identity classification: (Real IDs and fake)
- Pose classification: (Pose information)
- Loss
$$ \begin{aligned} \max_D V_D(D, G) &= E_{x,y \sim p_d (x,y)} [\log D^d_{y^d} (x) + \log D^p_{y^p} (x)] & \\ &+ E_{x,y \sim p_d (x,y), z \sim p_z(z), c \sim p_c(c)} [\log(D^d_{N^d+1} (G(x,c,z)))] & \end{aligned} $$
- First-term: 입력 영상에 대해서 그의 supervised label인 -identity와 -pose로 분류가 되도록
- Second-term: 생성된 faks 영상에 대해서 -번째 label(즉 fake label)로 분류가 되도록
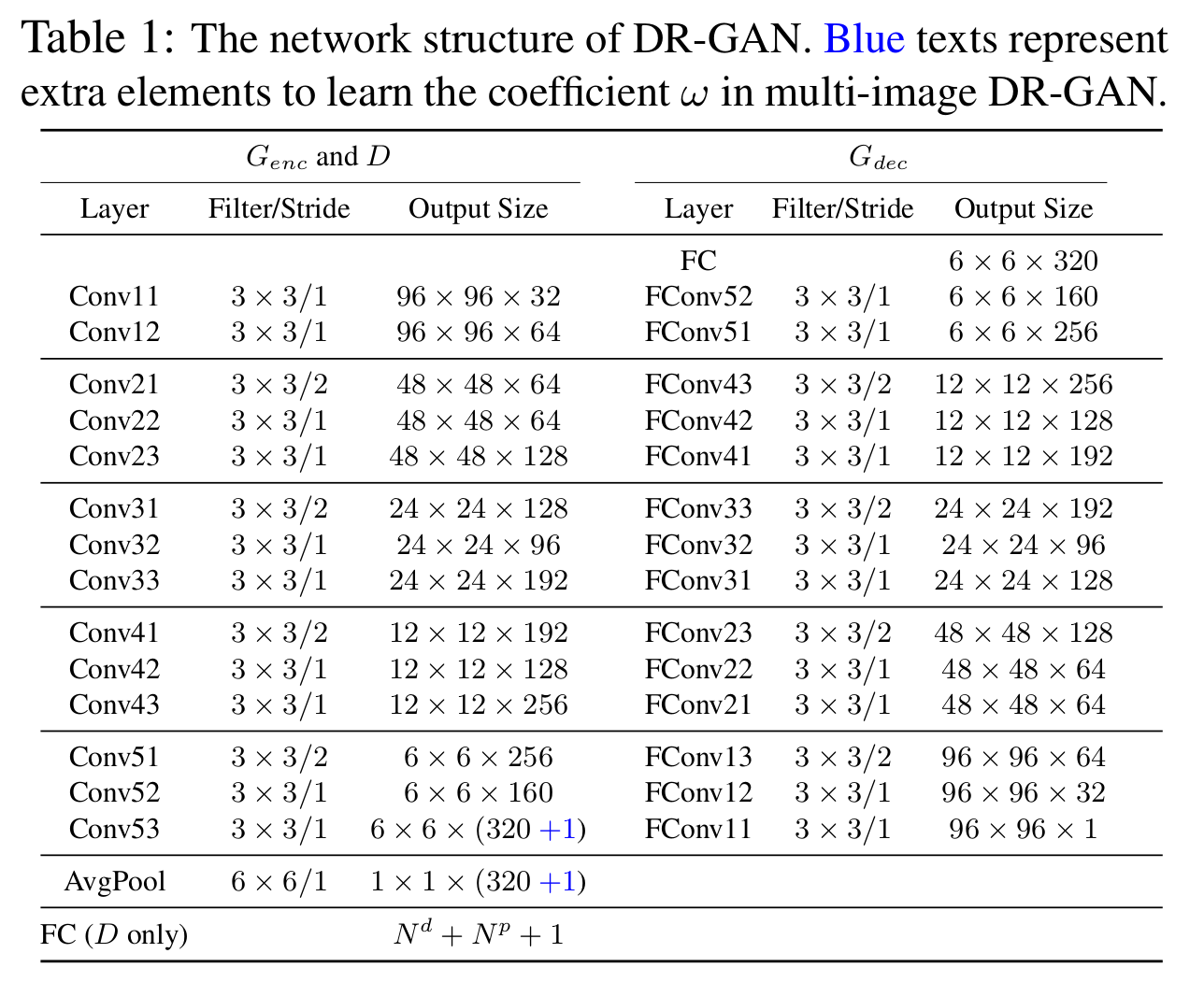
Generator
$$G_{enc}, G_{dec}$$
- Encoder: CASIA-Net[6]기반 매 conv이후에 BN, exp liner unit(ELU)적용하고 마지막에 avg. pool. 하면 최종적으로 latent vector 출력
- Decoder: 320-dim의 latent vector에 one-hot vector인 pose code 와 랜덤 노이즈 벡터 를 추가하여 입력하고 FConv[7] 이용하여 H,W를 키운다.
- Loss
$$ \max_G V_G (D,G) = E_{x,y \sim p_d (x,y)} [\log(D^d_{y^d} (G(x,c,z))) + \log(D^p_{y^t} (G(x,c,z)))] $$
- First-term: 생성된 영상이 real identity를 같도록 generator 학습
- Second-term: 생성된 영상이 원하는 타겟 포즈 를 갖도록 학습 (에만 1인 one-hot vector가 ) 해당 포즈로 생성되도록 잘 가이드를 해주며, 이 과정에서 는 pose-invariant 표현을 학습한다.
[네트워크 구조]
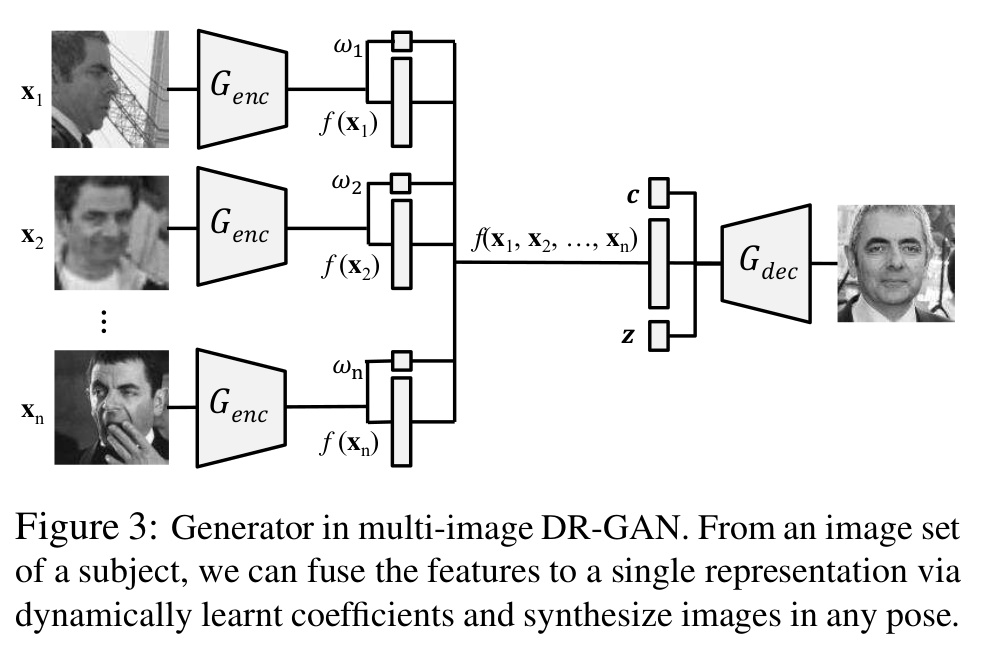
Multi-image DR-GAN
- 영상이 다수 들어오면 각 영상마다 어느정도의 웨이트를 주어야 하는지 학습한다. (face recognition을 위한 quality라고 볼 수 있다.)
- 따라서 320+1 dimension이 학습되며, decoder에 들어가기 전 최종 latect vector는 모든 얼굴영상 feature에 대해서 weighted sum을 수행하여 320-dimension으로 계산된다.
- G에 대한 loss-term이 약간 수정된다.
- 모든 입력 영상(n개)에 해당하는 z에 대해서 각각 타겟 포즈로 생성된 영상에 대한 pose, identity loss (2n개)
- 모든 입력 영상이 융합된 특징 벡터 z에 대해서 타겟 포즈로 생성된 영상에 대한 pose, identity loss (2개)
- 모든 는 파라미터를 공유한다.
- Weight는 [0,1]의 범위를 유지하기 위해서 sigmoid activation을 적용한다.
[Multi-image DR-GAN]
Training
- 기존의 GAN과 다르게 D에 supervision(class label이 있기에)이 강해 D가 optimal solution에 가까워졌을 때, G를 D보다 더 자주(4배) 업데이트한다.
- Pose label 이 없는 경우 3D face alignment를 적용하여 포즈를 이산적으로 분류한다.
- DC-GAN을 기반으로 코드를 수정하였다.
- Batch size는 64이다.
Experimental results
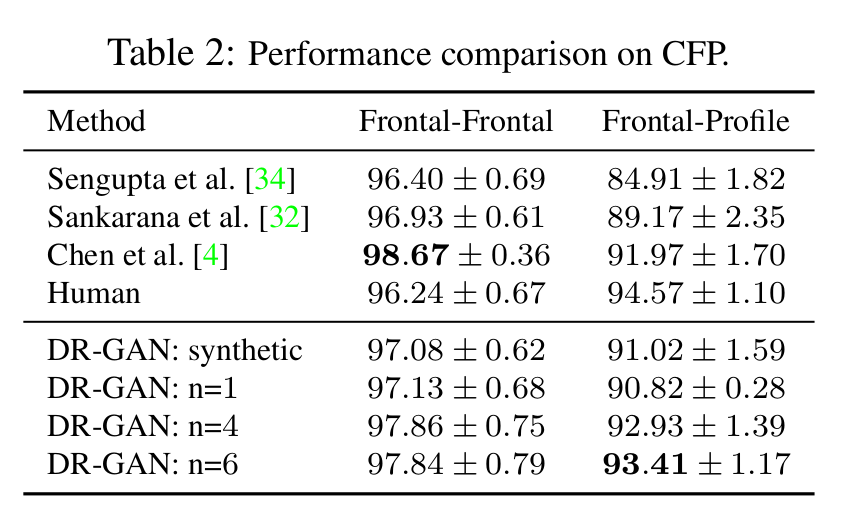
- 얼굴인식 성능
- F-F는 기존 방식보다 약간 낮지만, F-P는 기존보다 높다(근데 n=1일때는 더 낮다는 맹점)
- 영상을 많이 쓸수록 성능이 높다.
- DR-GAN:synthetic은 합성 영상을 pretrained face recognition model에 입력하여 identity feature를 사용하는 방법 (?)
[얼굴인식 성능]
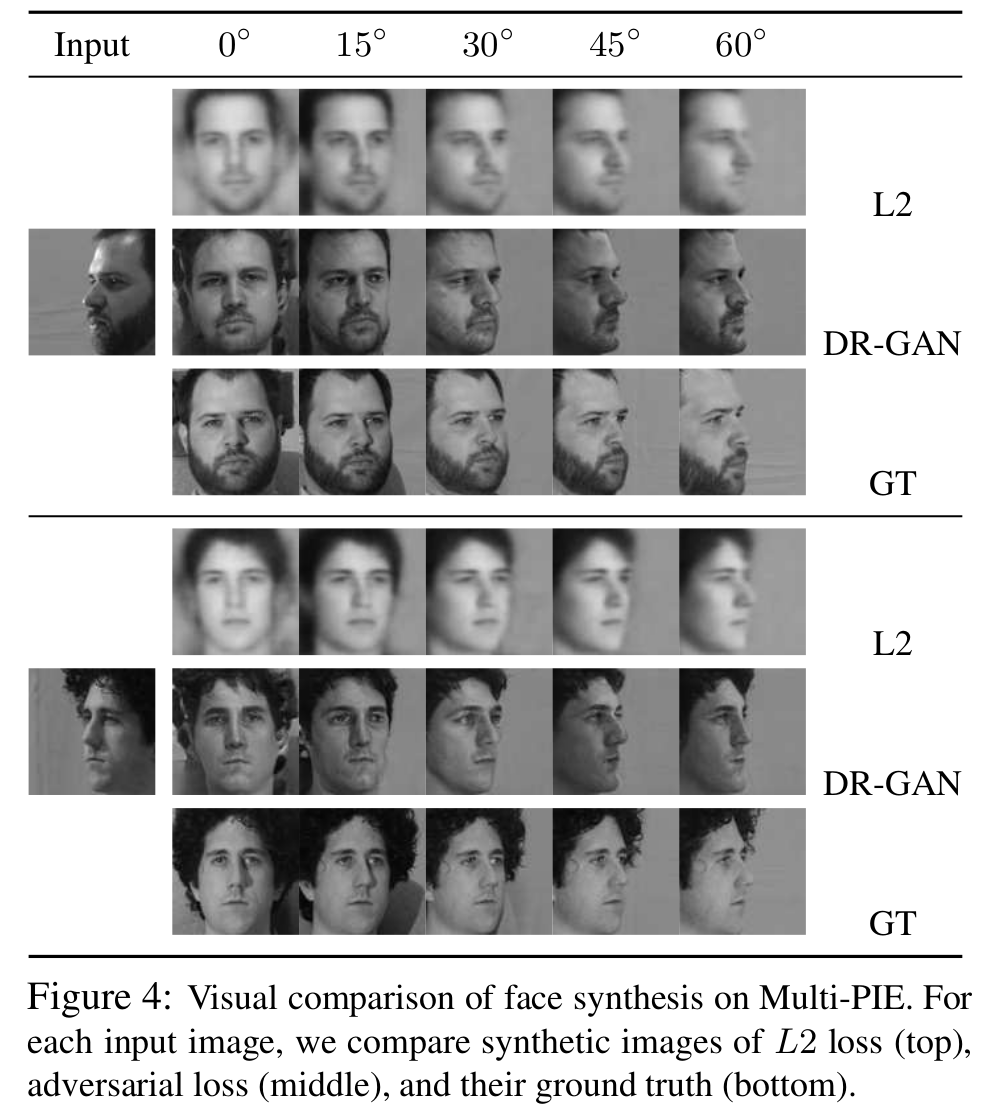
- Loss 비교
- L2 loss는 많이 뭉개지며 합성 결과가 좋지 않다.
[L2 loss와 adversarial loss의 시각적인 비교]
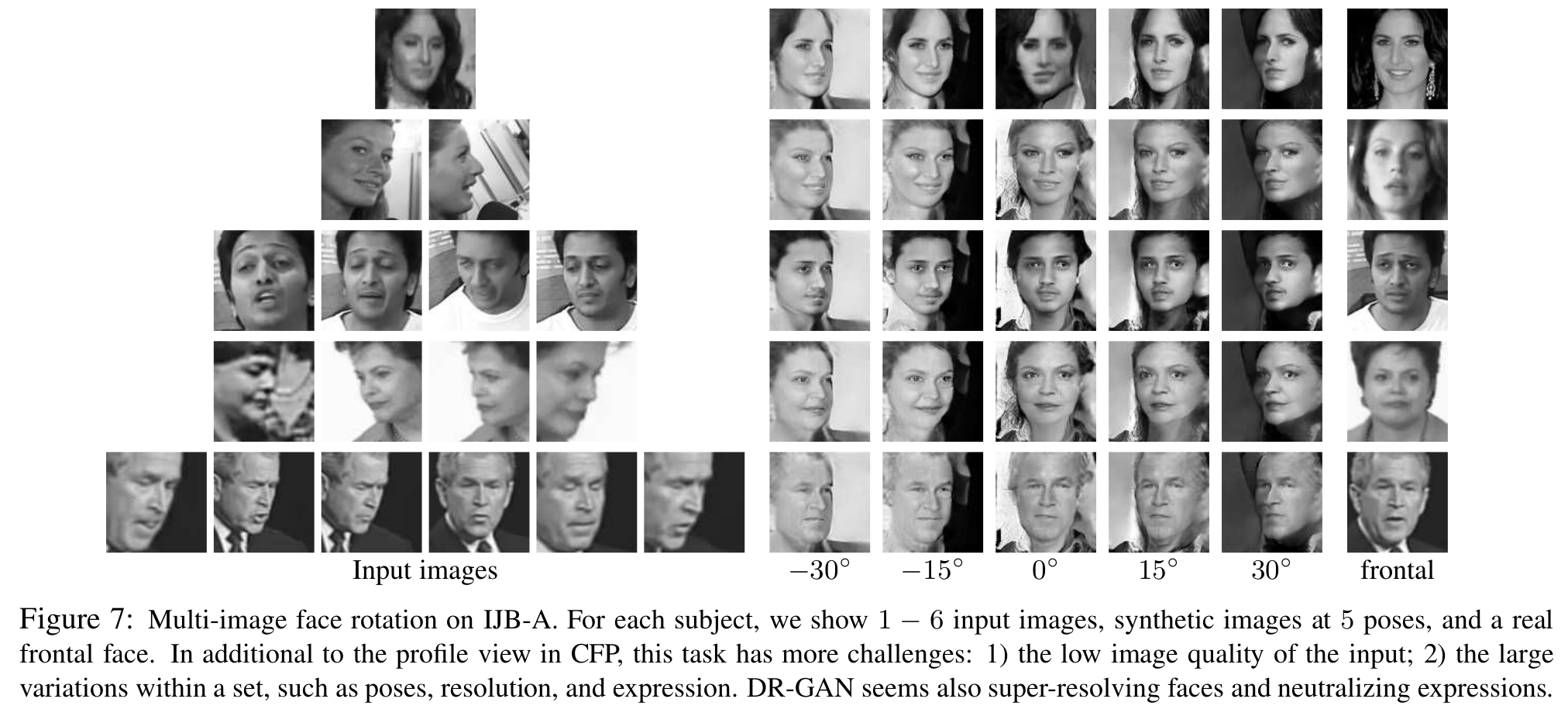
- 얼굴 합성 결과
- 영상의 수가 적으면 더 challenging한 것을 보임
[각도별 합성 결과(입력영상 1~6개)]

Comments
- Pose를 강제적으로 나누는 과정에서 성능이 감소했을수도..
- Pose/illumination 등 prior knowledge를 선택하는 것도 중요
- 완전한 disentangle이 안된다면 분명 놓치는 정보가 있을 것이다.
- Two-stage (영상 합성-data augmentation 영상 인식)이 아닌 one-stage에서 오는 문제점도 있을까?
References
[1] Tran, Luan, Xi Yin, and Xiaoming Liu. “Disentangled representation learning gan for pose-invariant face recognition.” Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2017.
[2] H. Kwak and B.-T. Zhang. Ways of conditioning generative adversarial networks. In NIPSW, 2016.
[3] M. Mirza and S. Osindero. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprint:1411.1784, 2014.
[4] J. T. Springenberg. Unsupervised and semi-supervised learning with categorical generative adversarial networks. ICLR, 2016.
[5] A. Makhzani, J. Shlens, N. Jaitly, and I. Goodfellow. Adversarial autoencoders. ICLRW, 2015.
[6] D. Yi, Z. Lei, S. Liao, and S. Z. Li. Learning face representation from scratch. arXiv preprint:1411.7923, 2014.
[7] A. Radford, L. Metz, and S. Chintala. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. ICLR, 2016.