[2019 CVPR] Unsupervised Part-Based Disentangling of Object Shape and Appearance
Table of content (full-version) [paper] [project page]
Summary
[요약]
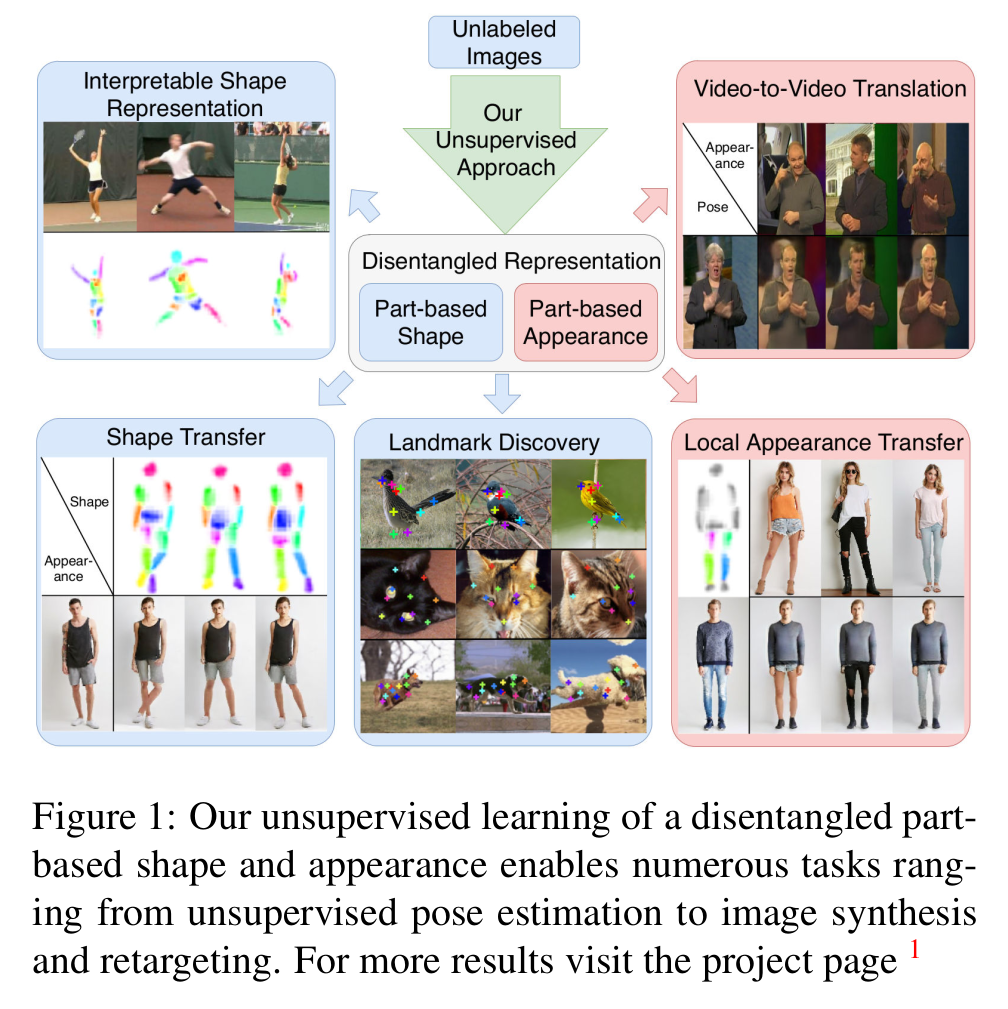
- Unsupervised 방식(파트정보 x, label x)으로 물체의 파트를 분할하여 모양과 외형을 분리하는 방법 (자동으로 물체의 구조적인 파트들을 구분지음)
- 여러가지 응용에서 사용가능
- Shape: interpretable shape representation, shape transfer, landmark discovery
- Appearance: local appearance transfer, video-to-video translation
- image pair 대신에 인위적인 변형으로 a/p를 구분할 수 있다는 장점
Architecture
[Notation]
| Symbol | Mean |
|---|---|
| image transformation (changes in brightness, contrast, hue) | |
| spatial image transformation (thin plate spline transformation) | |
| part-based factorization | |
| disentangled representation | |
| part appearance (feature vector) | |
| part shape (activation map) | |
| appearance hourglass network | |
| shape hourglass network | |
| decoder |
[전체 프레임워크]
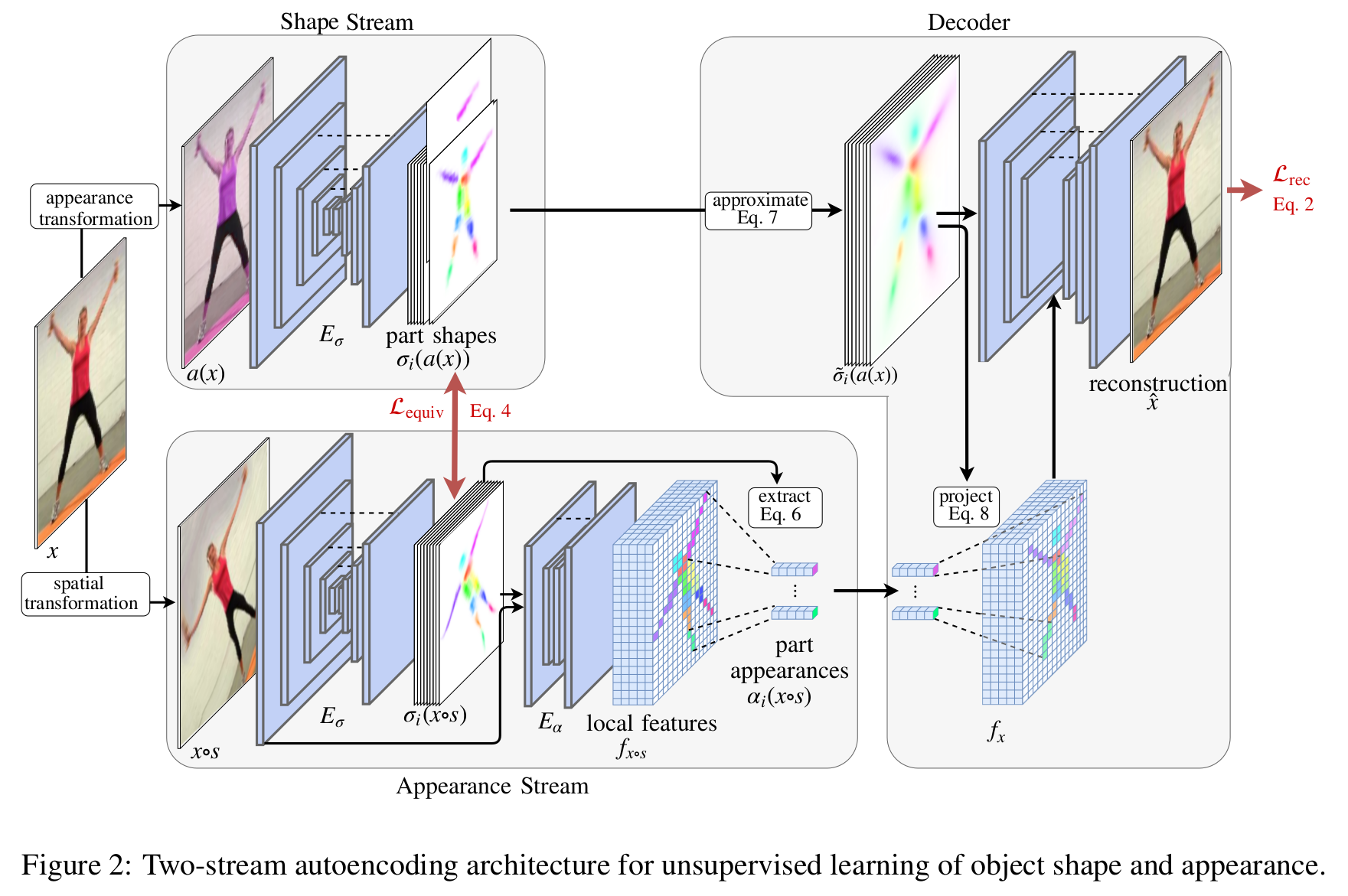
Shape stream
$$\sigma_i (a(x)) = \sigma_i (x)$$
- 영상의 appearance 변화시켜도 shape 관련 특징 유지 (invariant to appearance)
- 영상의 appearance를 에 의해 변화시킨 다음 shape hourglass network를 통과시켜 part shape activation map을 생성
- Hourglass network는 pixel-wise locality를 보존하고 multiple scale로 부터 정보를 통합한다는 점에서 이 task에 적합하다.
Appearance stream
$$\alpha_i (x \circ s) = \alpha_i (x)$$
- 영상의 shape 변해도 appearance 관련 특징 유지 (invariant to shape)
- 영상의 shape를 에 의해 변화시킨 다음 shape hourglass network를 통과시켜 part shape activation map을 생성
- 정규화된 part shape activation map과 영상의 일부 인코딩된 것(의 첫번째 conv filter의 출력 값)을 합친 다음 appearance hourglass network를 통과시켜 localized image appearance encoding 을 얻는다.
$$\alpha_i (x \circ s) = \frac{\sum_{u \in I} f_{x \circ s} [u] \sigma_i (x \circ s)[u]}{\sum_{u \in I} \sigma_i (x \circ s)[u]}$$
- 이를 average pool 하여 최종 part appearance feature vector를 얻는다.
Decoder
- U-Net을 사용 (인코더는 고정, 디코더만 학습)
$$\tilde{\sigma}_i (a(x)) [u] = \frac{1}{1 + (u - \mu_i)^T \Sigma^{-1}_i (u - \mu_i)}$$
- (첫 번째 입력) 부가정보를 무시하고 모호하지않은 part localization에 집중하기 위해서 part activation approximation
$$f_x [u] = \sum_i \frac{\alpha_i (x \circ s) \cdot \tilde{\sigma}_i (a(x))[u]}{1 + \sum_j \tilde{\sigma}_j (a(x))[u]} $$
- (두 번째 입력) 위의 part activation approximation을 이용하여 part appearance feature 의 위치를 잡아준다. (part appearance feature는 part별 average pooling 과정에 의해서 위치 정보가 없기 때문)
- 결국 shape stream의 위치 정보(invariant to appearance)와 appearance stream의 외형 정보(invariant to shape)를 통합하고 이를 U-Net에 거쳐 원래 영상으로 복원시킨다.
Equivalance loss
$$L_{equiv} = \sum_i \lambda_{\mu} \left \| \mu[\sigma_i (x \circ s)] - \mu[\sigma_i (a(x)) \circ s] \right \|_2 + \lambda_{\Sigma} \left \| \Sigma[\sigma_i (x \circ s)] - \Sigma[\sigma_i (a(x)) \circ s] \right \|_1 $$
- Equivariance:
- 각 파트별로 shape 변화시키면 shape 관련 특징 도 그만큼 변화해야 한다는 성질
- 각 파트별로 엑티베이션 평균 위치와 공분산 이용
Reconstruction loss
$$L_{rec} = \left \| x - D([\alpha_i (x \circ s), \sigma_i (a(x))]_{i=1,...} ) \right \|$$
- Invariance: and
- Invariance constraint 하에서 복원이 잘 되는지
Experimental results
- 파트의 수를 정하는 것은 중요하다.
- Landmark를 regression을 위한 분야가 아닌 이미지 합성을 하는 task에서는 영상을 진짜같이 만드는 것이 중요하므로 decoder에 adversarial loss를 추가한다. (real/fake 판단)
[Unsupervised landmark discovery]

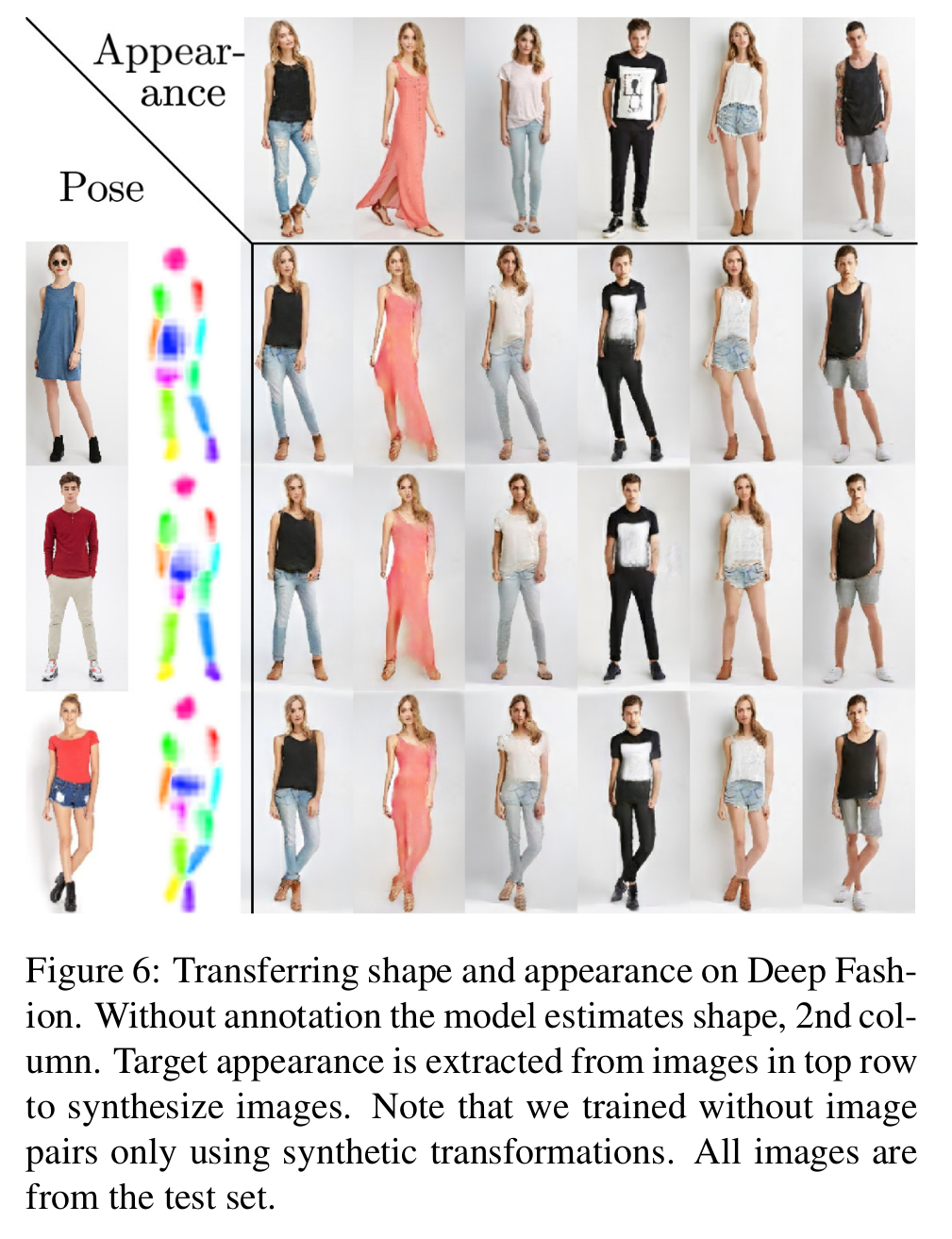
[사람의 Pose/appearance 디코딩 시각화(이미지)]
- Video-to-video translation
- Temporal consistency constraint가 없는데도 불구하고 시간축으로 움직임이 부드러우며 강인하다.
[사람의 Pose/appearance 디코딩 시각화(비디오)]

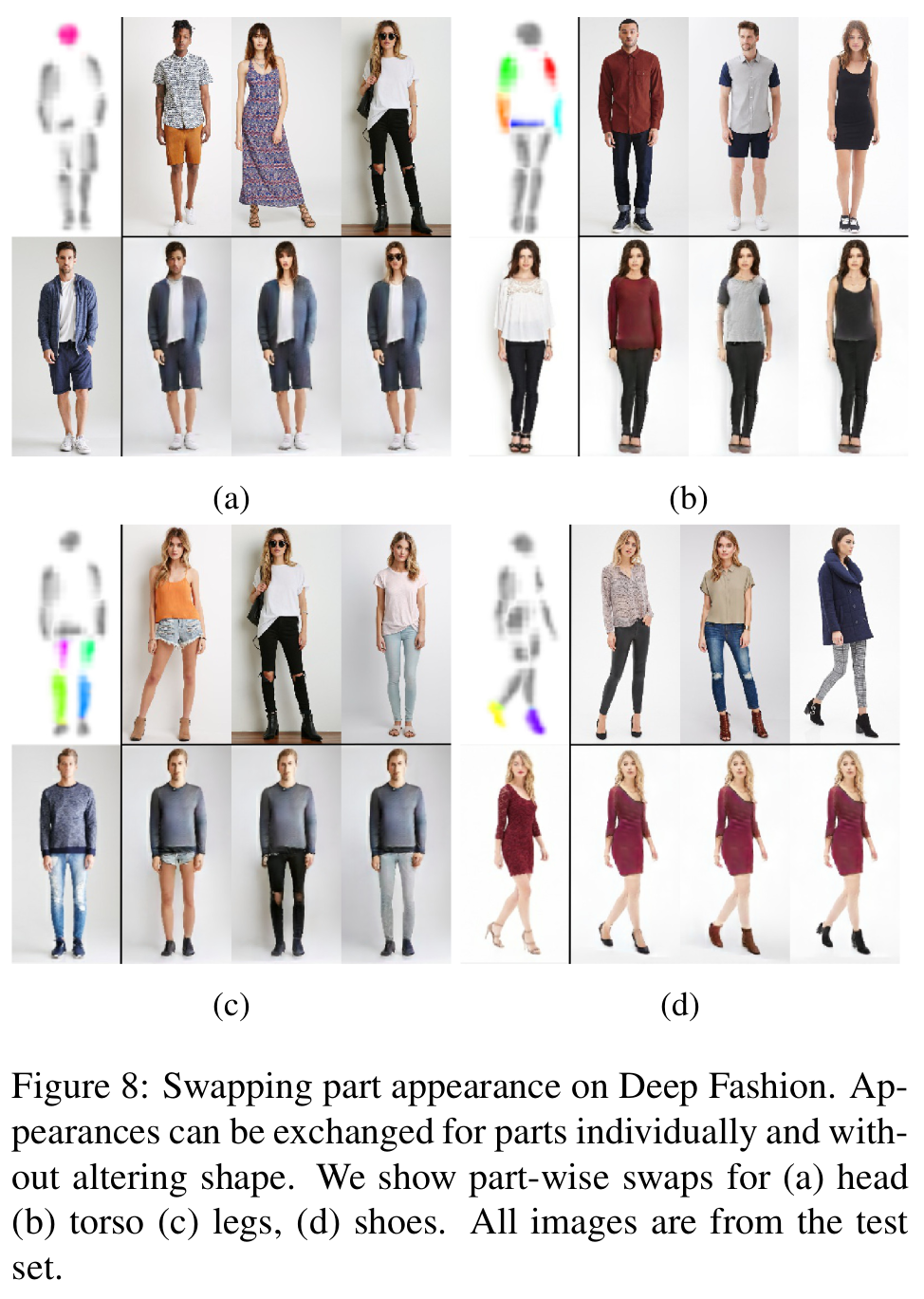
[사람의 일부 part만 변형 시각화]

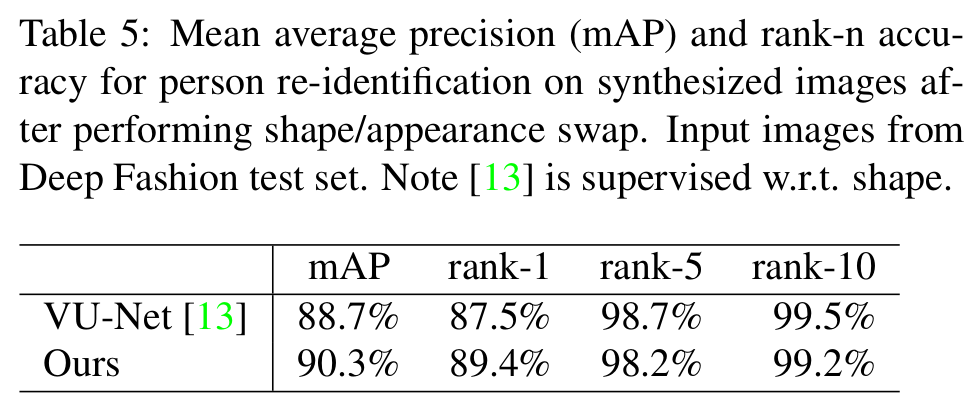
- Re-identification 으로의 적용
- Pretrained Inception-Net with [2] via triplet loss to Deep fashion DB
- Test set도 deep fashion
- VU-NET은 supervised 방식
[Re-Identification으로의 적용 결과]
Comments
- Image pair가 없어도 된다는점, unsupervised manner라는 점이 큰 장점
References
[1] Lorenz, Dominik, et al. “Unsupervised Part-Based Disentangling of Object Shape and Appearance.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.06946 (2019).
[2] T. Xiao, S. Li, B. Wang, L. Lin, and X. Wang. Joint detection and identification feature learning for person search. In CVPR. IEEE, 2017.